Linux Networking Tools
One can use a variety of network tools to perform tasks such as obtaining information about other systems on your network, accessing other systems, and communicating directly with other users. Network information can be obtained using utilities such as ping, finger, traceroute, host, dig, nslookup etc. These are useful for smaller networks and enables to access remote systems directly to copy files or execute the command.
Network Information Tools are listed below:
- ping: The ping command is used to check if a remote system is running or up. In short this command is used to detect whether a system is connected to the network or not.
Syntax:$ ping www.geeksforgeeks.com

Note: In place of using domain name you can use IP address also. A ping operation can fail if ping access is denied by a network firewall.
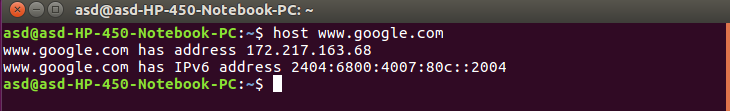
- host: This command is used to obtain network address information about a remote system connected to your network. This information usually consists of system’s IP address, domain name address and sometimes mail server also.
Syntax:$ host www.google.com
- finger: One can obtain information about the user on its network and the who command to see what users are currently online on your system. The who command list all users currently connected, along with when, how long, and where they logged in. finger can operate on large networks, though most systems block it for security reasons.
Syntax:$ finger www.ABC.com
In place of ABC you can use any website domain or IP address.
- traceroute: This command is use to track the sequence of computer networks. You can track to check the route through which you are connected to a host. mtr or xmtr tools can also be used to perform both ping and traces. Options are available for specifying parameters like the type of service (-t) or the source host (-s).
- netstat: This command is used to check the status of ports whether they are open, closed, waiting and masquerade connections. Network Statistic (netstat) command display connection information, routing table information etc.
Syntax:$ netstat
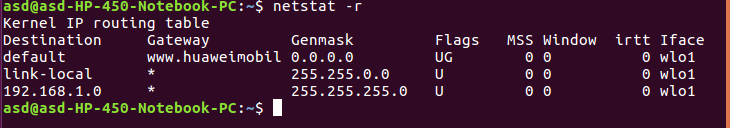
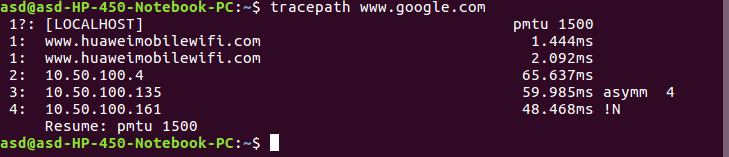
Note: To display routing table information use (netstat -r). - tracepath: tracepath performs a very similar function to that of traceroute command. The main difference between these command is that tracepath doesn’t take complicated options. This command doesn’t require root privileges.
Syntax:$ tracepath www.google.com
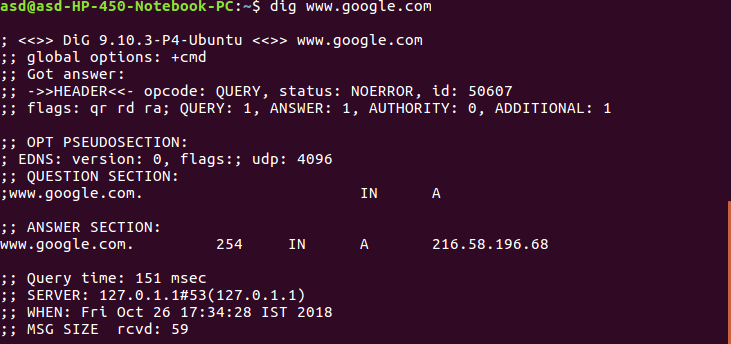
- dig: dig(Domain Information Groper) query DNS related information like a record, cname, mxrecord etc. This command is used to solve DNS related queries.
Syntax:$ dig www.google.com
- hostname: This command is used to see the hostname of your computer. You can change hostname permanently in etc/sysconfig/network. After changing the hostname you need to reboot the computer.
Syntax:$ hostname

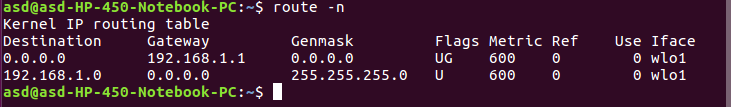
- route: The route command is used to display or modify the routing table. To add a gateway use (-n).
Syntax:$ route -n
- nslookup: You can use nslookup(name server lookup) command to find out DNS related query or testing and troubleshooting DNS server.
Syntax:$ nslookup google.com
Join the conversation